The Myth of Eating Fat Makes You Fat
For years, the belief that consuming fat leads to weight gain has shaped our understanding of nutrition. This myth makes it seem simpler than it is.
You will explore the origins of this misconception and uncover the essential roles that fat plays in our bodies, along with the different types of fat and their effects on health.
By the end of this journey, you ll confidently embrace healthy fats in your diet and debunk outdated notions for a more balanced approach to eating!
Contents
Key Takeaways:

- Eating fat does not necessarily make you gain weight.
- The idea that fat consumption leads to weight gain is a myth backed by recent research.
- Dietary fat plays vital roles in the body, such as providing energy and aiding nutrient absorption.
- Including healthy fats can positively affect your overall health.
- Not all fats are created equal. Excessive unhealthy saturated fats may lead to weight gain and health issues, while unsaturated fats from recommended sources can be beneficial when consumed in moderation.
Understanding the Myth
Recently, you may have noticed a lively debate regarding saturated fat and its links to heart disease, capturing the attention of nutrition experts and health organizations.
Some assert that saturated fat is inherently detrimental, contributing to high cholesterol and an increased risk of heart disease. Others argue that the relationship is far more complex.
This dialogue often involves the influence of the food industry and dietary guidelines aimed at protecting public health. As you explore this topic, consider a range of perspectives from evidence-based research and nutrition studies for a comprehensive understanding of dietary practices today.
Where Did the Idea Come From?
The idea that saturated fat is linked to heart disease dates back to early nutrition studies that suggested a direct correlation between high saturated fat intake and elevated cholesterol levels, both recognized as risk factors for cardiovascular issues.
During the mid-20th century, this narrative gained traction, especially through influential research like the Framingham Heart Study, which reinforced the belief that dietary fat could negatively impact heart health.
Food marketing strategies of the time propagated this perspective, promoting low-fat products while ignoring the complexities of dietary fats. Organizations such as the American Heart Association initially advocated for reducing saturated fat consumption.
However, as new studies emerged, their recommendations evolved. They began to recognize the intricate nature of fat sources and the importance of overall dietary patterns rather than solely focusing on specific nutrients.
This evolution signifies a broader understanding of how food choices affect health, challenging earlier beliefs that simplified the relationship between fat and heart disease.
The Role of Fat in the Body
Fats play a crucial role in your body, serving as a primary energy source, supporting cell growth, and facilitating the absorption of essential vitamins.
A balance of healthy fats, including unsaturated and saturated fats, is necessary to maintain overall health and well-being.
By understanding how these dietary fats influence cholesterol levels and long-term health, you can make more informed food choices.
Nutrition experts emphasize the importance of distinguishing between different types of fats and recognizing their unique impacts on health, especially when considering evidence-based nutritional guidelines.
Functions and Importance of Dietary Fat
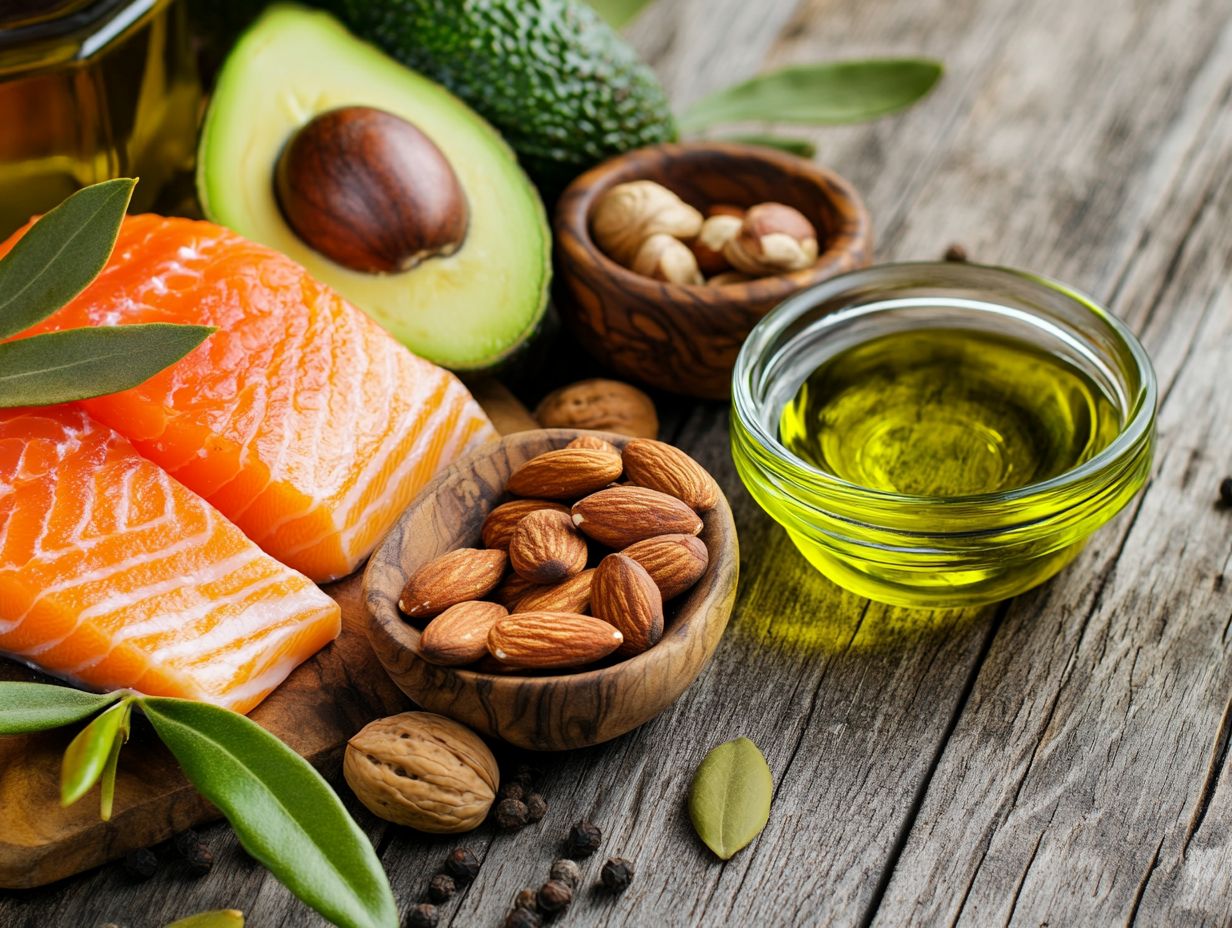

Dietary fat is essential for a variety of bodily functions, including providing energy, supporting cell structure, and facilitating the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Unsaturated fats found in tasty foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil can help reduce the risk of heart disease. They also promote overall cardiovascular health.
On the flip side, saturated fats, often lurking in animal products and certain oils, can affect cholesterol levels and cardiovascular risk when consumed in excess.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial. By incorporating the right types of fats into your diet, you can enhance your energy levels and improve nutrient absorption.
These fats are not just a luxury; they play a pivotal role in hormone production and maintaining cellular integrity. This makes them critical to a well-rounded diet.
Types of Fat and Their Effects on the Body
Understanding the various types of dietary fats saturated, unsaturated, polyunsaturated, and monounsaturated is essential for making informed health decisions.
Recognizing how each type impacts your body can empower you to choose wisely, leading to a healthier lifestyle.
Saturated vs. Unsaturated Fat
Saturated fat, often found in red and processed meats, stands in stark contrast to unsaturated fat, which predominantly resides in plant-based oils, nuts, and fish. This distinction is significant due to their varying impacts on health and cholesterol levels.
Understanding the health implications of these fats is crucial for making informed dietary choices. Research consistently indicates that saturated fats can elevate levels of LDL cholesterol, often called ‘bad’ cholesterol, thus heightening the risk of heart disease.
Conversely, unsaturated fats have been shown to lower LDL cholesterol while boosting HDL cholesterol, known as ‘good’ cholesterol, ultimately promoting heart health.
This distinction is especially important, as dietary guidelines advocate for prioritizing unsaturated fats to support cardiovascular wellness. They suggest that saturated fats be consumed in moderation.
Despite this knowledge, misconceptions linger. Many still believe that all fats are detrimental; however, the key lies in selecting the right types to achieve a well-balanced diet.
Debunking the Myth
Recent research is starting to challenge the long-held belief that saturated fat is a primary culprit behind heart disease.
It suggests that the connection between fat consumption and health risks is far more complex than previously believed.
Recent Research and Evidence

A growing body of nutrition studies suggests that the impact of saturated fat on heart disease may hinge more on your overall dietary patterns than on fat consumption alone.
Recent research has shed light on how the combinations of different foods, rather than just isolated nutrient intakes, play a pivotal role in your cardiovascular health.
For example, one study revealed that individuals consuming saturated fats within a diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains showed fewer markers of heart disease compared to those indulging in high amounts of processed foods, even with similar saturated fat intake.
Expert panels are starting to embrace these findings, leading to a shift in health recommendations that now prioritize holistic dietary approaches over the mere restriction of singular nutrients.
This transition reflects a growing understanding that the interplay between various food components can significantly shape your long-term health outcomes.
How to Incorporate Healthy Fats into Your Diet
Adding healthy fats to your meals can significantly boost your health! You can easily do this by making informed food choices that favor unsaturated fats over saturated fats.
Embracing this approach not only enhances your overall well-being but also supports your body’s essential functions. Make the switch today!
Recommended Sources and Serving Sizes
To incorporate healthy fats into your diet, focus on sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Keep an eye on those recommended serving sizes.
These foods elevate your meals and provide essential nutrients that support cardiovascular health while helping reduce inflammation.
For instance, enjoying a serving of avocado about one-third of a medium fruit gives you nearly 10 grams of healthy fat for your heart.
A handful of nuts, around 1 ounce, delivers beneficial fatty acids, protein, and fiber, promoting fullness and assisting with weight management.
Seeds like chia or flaxseeds are also great options; adding just a tablespoon to your smoothies or oatmeal can provide a significant omega-3 boost.
By selecting these healthy options and balancing them with other dietary fats, you can cultivate a diverse and nutritious eating pattern that aligns with your health goals, facilitating long-term wellness and vitality.
Frequently Asked Questions
Busting the Myth: Does Fat Make You Fat?

The myth that eating fat makes you fat is the belief that consuming high-fat foods leads to weight gain or obesity. This misconception has been perpetuated for decades, and understanding what are the myths about fats can help clarify why fat has been demonized in the diet.
Is There Any Truth to This Myth?
No, there is no scientific evidence supporting the myth that eating fat makes you fat. In fact, consuming healthy fats in moderation can be beneficial for weight management and overall health.
Why Do People Believe This Myth?
People often believe that eating fat makes you fat because it contains more calories per gram compared to protein and carbohydrates. This led to the assumption that consuming fat would automatically lead to weight gain.
What Are Some Healthy Sources of Fat?
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds
- Fatty fish like salmon
- Olive oil
- Coconut oil
These fats are packed with nutrients that keep you energized and satisfied when consumed in moderation.
How Can Consuming Too Little Fat Be Harmful?
Consuming too little fat can lead to nutrient deficiencies, as fat-soluble vitamins and essential fatty acids are found in fat sources. It can also negatively impact hormone production, energy levels, and overall health.
Can I Lose Weight by Including Healthy Fats in My Diet?
Yes, incorporating healthy fats into your diet can aid in weight loss. Fats help you feel fuller for longer, leading to reduced calorie intake. They also provide sustained energy, making it easier to maintain an active lifestyle and burn calories.
Ready to improve your diet? Start adding healthy fats to your meals today!